Handling alpha clipping with compute casters

Written by Jesper Tingvall, Product Expert, Simplygon
Disclaimer: The code in this post is written using version 10.4.272.0 of Simplygon. If you encounter this post at a later stage, some of the API calls might have changed. However, the core concepts should still remain valid.
Introduction
In this blog we will have a look at how to create billboard impostors for assets using shaders with alpha clipping. The solution is to introduce a little code snippet using sg_DiscardValue and sg_PreviousValue in every sampler function.
This blog is a continuation of Using your own shaders for material baking with Compute Casting and will use the same code skeleton. Only the new parts will be introduced, so reading the previous blog for a full understanding is recommended.
Prerequisites
This example will use the Simplygon Python API, but the same concepts can be applied to all other integrations of the Simplygon API. Our shaders are specified in HLSL but it is also possible to use GLSL. Compute casters can be used with any pipeline using material casting.
Problem to solve
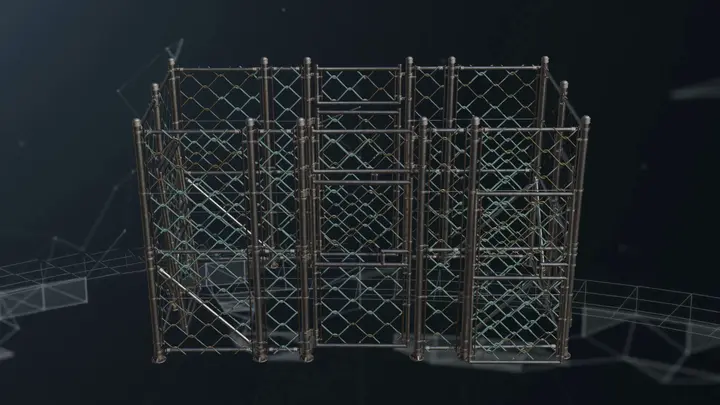
We want to optimize a fence like structure based on this modular chainlink fence model. The fence wires is not made using geometry, it uses a texture with alpha clipping.
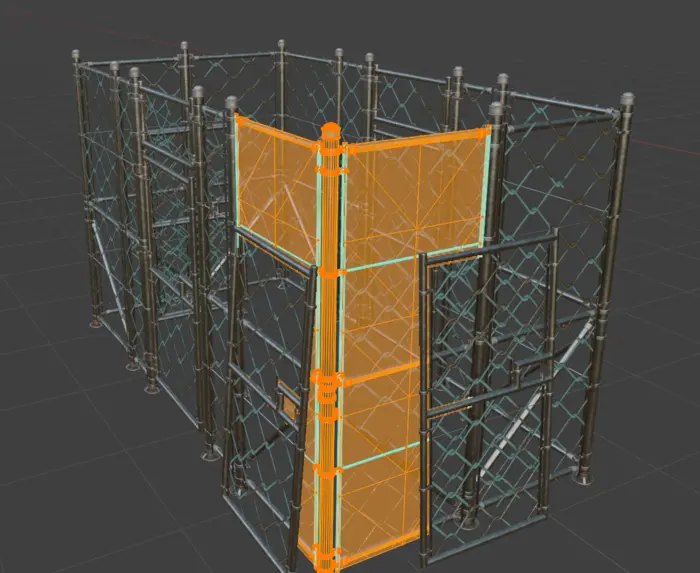
The assets are saved with normals, tangents and bitangents vertex attributes. This data is needed to cast the tangent-space normal map. If your input assets does not contain this data the normal map output will be empty when casting normal map.
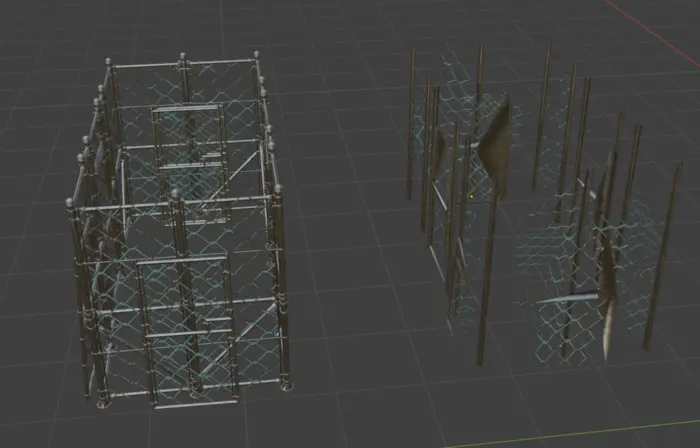
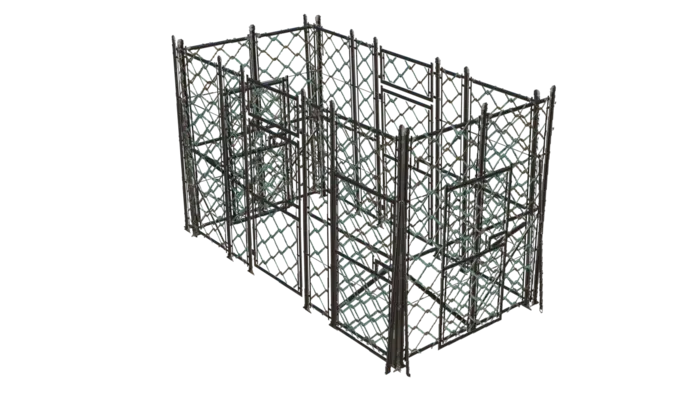
If we try to use our ordinary reducer we get a not so good optimization at low triangle counts. Here we tried to optimize it down to 300 triangles and the result is a mess.
Instead of using triangle reduction we are going to create a billboard impostor and use compute casters to bake the materials to it.
Solution
We are going to use the same solution structure as our previous blog with an xml describing the material casting per asset. What we are going to change is add a billboard pipeline, change how we create compute casters and add a new shader for alpha clipped assets.
Billboard pipeline
We start with a helper function that creates a billboard cloud pipeline and set quality settings.
def create_billboard_pipeline(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, density: float, planeComplexity: float, max_plane_count: int, textureSize: int):
pipeline = sg.CreateBillboardCloudPipeline()
settings = pipeline.GetBillboardCloudSettings()
settings.SetMaxPlaneCount(max_plane_count)
settings.SetBillboardDensity(density)
settings.SetGeometricComplexity(planeComplexity)
Simplygon can use the material's opacity channel to make the planes fit tighter. To do this we need to set the correct opacity settings, same as in the material configuration xml file. This is described in more details in the blog post Tight fitting impostors with minimal overdraw.
settings.SetOpacityChannel("Diffuse")
settings.SetOpacityChannelComponent(Simplygon.EColorComponent_Alpha)
settings.SetOpacityCutoff(0.5)
We also enable creation of a mapping image which is required to cast textures to our proxy. One setting worth highlighting is MaximumLayers which we always suggest setting high when you have asset that contains materials with alpha clipping or transparency.
mapping_image_settings = pipeline.GetMappingImageSettings()
mapping_image_settings.SetGenerateMappingImage(True)
mapping_image_settings.SetGenerateTexCoords(True)
mapping_image_settings.SetGenerateTangents(True)
mapping_image_settings.SetUseFullRetexturing(True)
mapping_image_settings.SetApplyNewMaterialIds(True)
mapping_image_settings.SetMaximumLayers(10) # When doing billboard impostors we always suggest to use high maximum layer counts
mapping_image_settings.SetTexCoordName("MaterialLOD")
mapping_image_settings.GetOutputMaterialSettings(0).SetTextureHeight(textureSize)
mapping_image_settings.GetOutputMaterialSettings(0).SetTextureWidth(textureSize)
mapping_image_settings.GetOutputMaterialSettings(0).SetMultisamplingLevel(2)
mapping_image_settings.GetOutputMaterialSettings(0).SetGutterSpace(4)
return pipeline
After processing the asset with out billboard pipeline this is the output geometry. We can see that we have double geometry along the borders. This is because the asset is intended to be rendered with back face culling. Pay attention to that the loose doors that are leaning towards the fence cell are now part of the same billboard as wall.
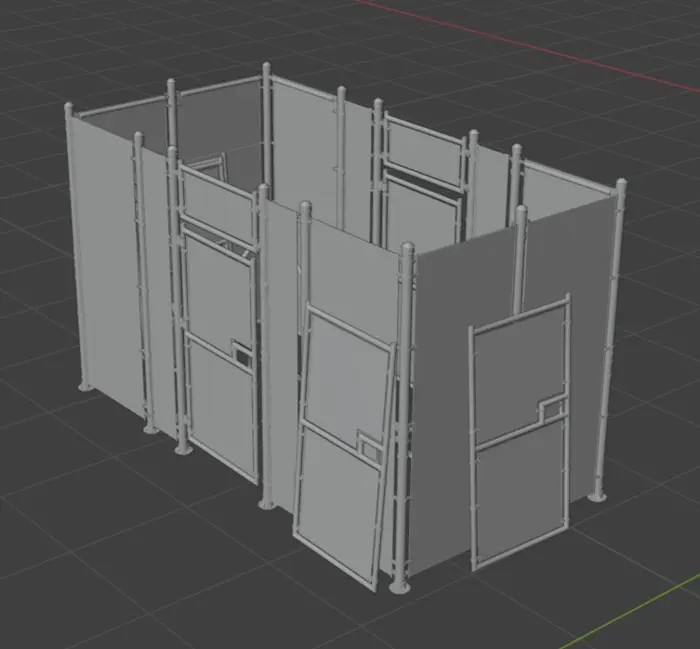
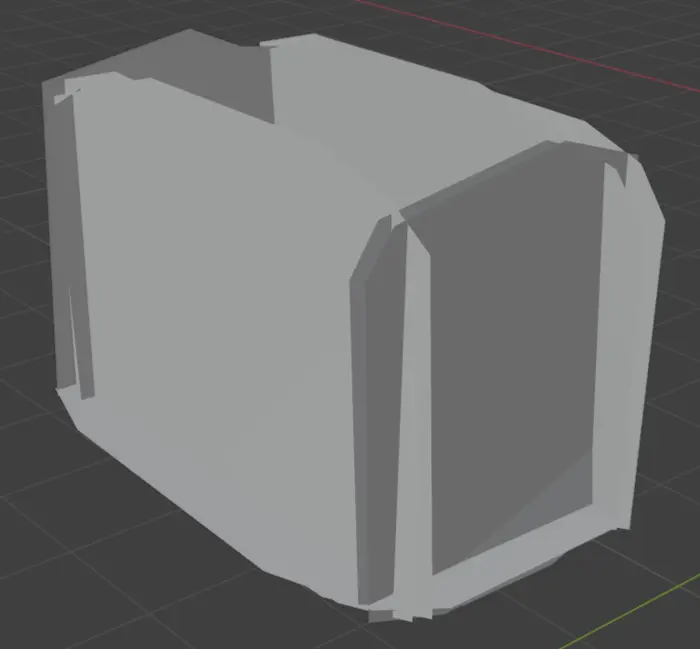
Compute casters
Our different textures will contain different data that requires different pixel formats. So we extend out create_compute_caster function so we can specify options in more detail.
def create_compute_caster(sg : Simplygon.ISimplygon, channel_name : str, color_space, fill_mode, dilation, output_pixel_format, output_path : str) -> Simplygon.spComputeCaster:
"""Create compute caster for specified channel and color space."""
print(f"Creating compute caster for {channel_name}")
caster = sg.CreateComputeCaster()
caster.SetOutputFilePath(output_path)
caster_settings = caster.GetComputeCasterSettings()
caster_settings.SetMaterialChannel(channel_name)
caster_settings.SetOutputColorSpace(color_space)
caster_settings.SetOutputPixelFormat(output_pixel_format)
caster_settings.SetOutputImageFileFormat( Simplygon.EImageOutputFormat_PNG )
caster_settings.SetDilation(dilation)
caster_settings.SetFillMode(fill_mode)
return caster
The material channels are defined in this table.
- Diffuse is a SRBG texture with an alpha channel. This is the only texture that uses alpha. We set FillMode to NoFill. This means that pixels that remains unfilled after casting will be empty (black and transparent).
- Roughness and Metal are a linear textures. We fill the area outside by increasing Dilation and set FillMode to Interpolate. This makes so most of the texture is filled, and the areas where no casting was performed is interpolated between the nearby samples. This is useful for mip maps and avoiding color bleeding.
- Normals is our normal map. Normal maps should always be in linear color space. We also interpolate and dilate this texture.
MATERIAL_CHANNELS = [("Diffuse", Simplygon.EImageColorSpace_sRGB, Simplygon.EAtlasFillMode_NoFill, 0, Simplygon.EPixelFormat_R8G8B8A8),
("Roughness", Simplygon.EImageColorSpace_Linear, Simplygon.EAtlasFillMode_Interpolate, 40, Simplygon.EPixelFormat_R8G8B8),
("Metal", Simplygon.EImageColorSpace_Linear, Simplygon.EAtlasFillMode_Interpolate, 40, Simplygon.EPixelFormat_R8G8B8),
("Normals", Simplygon.EImageColorSpace_Linear, Simplygon.EAtlasFillMode_Interpolate, 40, Simplygon.EPixelFormat_R8G8B8)]
Alpha cutout shaders
The shader evaluation functions needs to be extended with a little snipped of code that tells Simplygon if the value should be discarded.
There are two build in values we will use to add alpha clipping.
- sg_DiscardValue - When we set this to true the value is discarded.
- sg_PreviousValue - Accesses the previous layers value. The values are calculated from bottom to top. The value in sg_PreviousValue is the "total" calculated value of all layer below it. Here we just return the value as it is, but we could also use this to describe how alpha blending works in our shaders.
// Sample Diffuse texture for diffuse channel
float4 CalculateDiffuseChannel()
{
float4 color = DiffuseTexture.SampleLevel(DiffuseTextureSamplerState, TexCoord,0);
// If we have alpha less then cutoff value discard this value and instead use previous value.
if (color.a <= 0.5f) {
sg_DiscardValue = true;
return sg_PreviousValue;
}
return color;
}
For the other channels we introduce a similar snippet. It is important to notice that we always sample the Diffuse texture and compare it's alpha value, not the channel that we are currently casting. This is because it is that texture which contains the alpha data.
// Sample Metal texture
float4 CalculateMetalChannel()
{
// If we have alpha less then cutoff value discard this value and instead use previous value.
// Notice that we check the diffuse texture's alpha, not metal channel.
float4 color = DiffuseTexture.SampleLevel(DiffuseTextureSamplerState, TexCoord,0);
if (color.a <= 0.5f) {
sg_DiscardValue = true;
return sg_PreviousValue;
}
float4 metal = MetalTexture.SampleLevel(MetalTextureSamplerState, TexCoord,0);
return metal;
}
Here are the output textures. We can see in the diffuse texture that we have multiple surfaces that have been merged into one billboard.
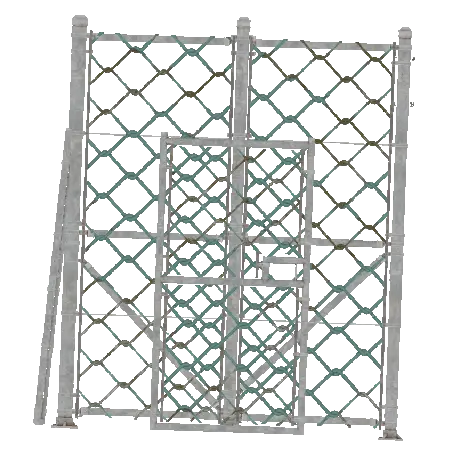
The normal map does not have an alpha channel, instead it is interpolating between the different samples in areas not casted to.
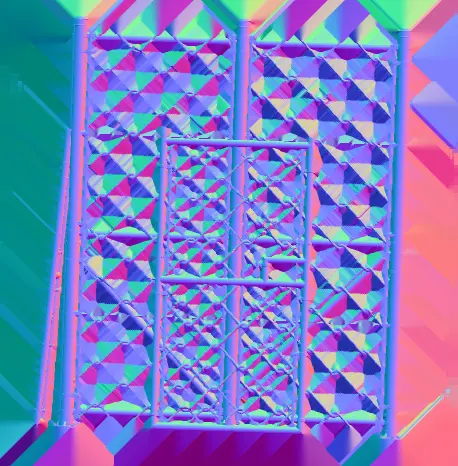

Result
Once we have all that up and running we can try out our new pipeline.
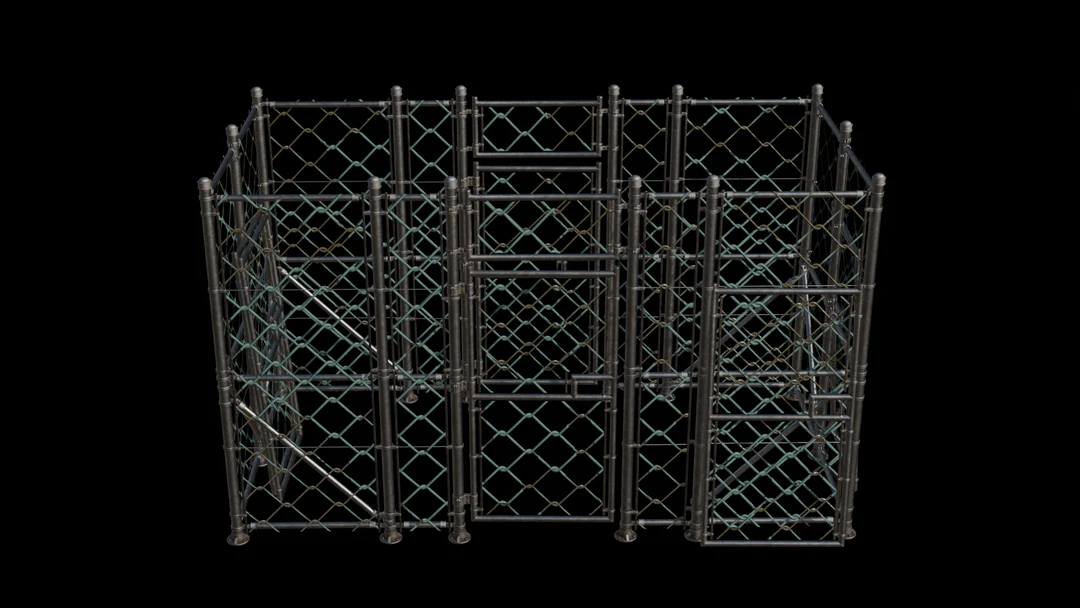


The surface is very similar to the original model and we can see in several places that we are using alpha clipping to map multiple wire-fence areas to the same billboard.
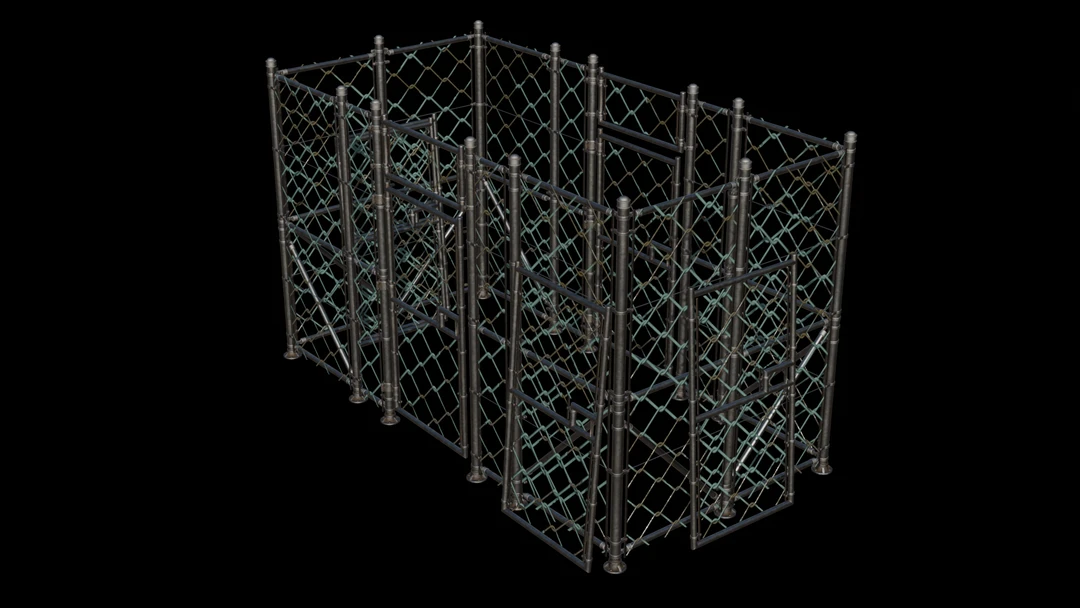

Our optimized proxy model is optimized in several ways that makes it ideal for render at a distance.
- It has extremely low triangle count and every triangle is large.
- It has very low overdraw.
- It uses only one material and set of textures. While this was not an issue with original model, it will always give us one material no matter the input material count.
| Model | Triangle count | Material count | Texture references |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 156 k | 2 | 8 x 4k textures |
| Billboard proxy | 62 | 1 | 4 x 2k textures |
Complete scripts
ComputeCasting.py
# Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.
# Licensed under the MIT License.
import gc
import os
from simplygon10 import simplygon_loader
from simplygon10 import Simplygon
# Channels to cast
# Tuple of: material name, output color space, fill mode, dilation, pixel format
MATERIAL_CHANNELS = [("Diffuse", Simplygon.EImageColorSpace_sRGB, Simplygon.EAtlasFillMode_NoFill, 0, Simplygon.EPixelFormat_R8G8B8A8),
("Roughness", Simplygon.EImageColorSpace_Linear, Simplygon.EAtlasFillMode_Interpolate, 40, Simplygon.EPixelFormat_R8G8B8),
("Metal", Simplygon.EImageColorSpace_Linear, Simplygon.EAtlasFillMode_Interpolate, 40, Simplygon.EPixelFormat_R8G8B8),
("Normals", Simplygon.EImageColorSpace_Linear, Simplygon.EAtlasFillMode_Interpolate, 40, Simplygon.EPixelFormat_R8G8B8)]
# Output settings
OUTPUT_FOLDER = "output"
OUTPUT_TEXTURE_FOLDER = f"{OUTPUT_FOLDER}/textures"
# Input settings
INPUT_FOLDER = "input"
FILE_ENDING = ".fbx"
def load_scene(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, path: str) -> Simplygon.spScene:
"""Load scene from path and return a Simplygon scene."""
scene_importer = sg.CreateSceneImporter()
scene_importer.SetImportFilePath(path)
import_result = scene_importer.Run()
if Simplygon.Failed(import_result):
raise Exception('Failed to load scene.')
scene = scene_importer.GetScene()
return scene
def save_scene(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, sgScene: Simplygon.spScene, path: str):
"""Save scene to path."""
scene_exporter = sg.CreateSceneExporter()
scene_exporter.SetExportFilePath(path)
scene_exporter.SetScene(sgScene)
print (f"Saving {path}...")
export_result = scene_exporter.Run()
if Simplygon.Failed(export_result):
raise Exception('Failed to save scene.')
def create_billboard_pipeline(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, density: float, planeComplexity: float, max_plane_count: int, textureSize: int):
"""Create a billboard cloud pipeline."""
pipeline = sg.CreateBillboardCloudPipeline()
settings = pipeline.GetBillboardCloudSettings()
settings.SetMaxPlaneCount(max_plane_count)
settings.SetBillboardDensity(density)
settings.SetGeometricComplexity(planeComplexity)
# Set correct opacity settings to make billboard edge closer to the alpha cutout parts.
settings.SetOpacityChannel("Diffuse")
settings.SetOpacityChannelComponent(Simplygon.EColorComponent_Alpha)
settings.SetOpacityCutoff(0.5)
mapping_image_settings = pipeline.GetMappingImageSettings()
mapping_image_settings.SetGenerateMappingImage(True)
mapping_image_settings.SetGenerateTexCoords(True)
mapping_image_settings.SetGenerateTangents(True)
mapping_image_settings.SetUseFullRetexturing(True)
mapping_image_settings.SetApplyNewMaterialIds(True)
mapping_image_settings.SetMaximumLayers(10) # When doing billboard impostors we always suggest to use high maximum layer counts
mapping_image_settings.SetTexCoordName("MaterialLOD")
mapping_image_settings.GetOutputMaterialSettings(0).SetTextureHeight(textureSize)
mapping_image_settings.GetOutputMaterialSettings(0).SetTextureWidth(textureSize)
mapping_image_settings.GetOutputMaterialSettings(0).SetMultisamplingLevel(2)
mapping_image_settings.GetOutputMaterialSettings(0).SetGutterSpace(4)
return pipeline
def create_compute_caster(sg : Simplygon.ISimplygon, channel_name : str, color_space, fill_mode, dilation, output_pixel_format, output_path : str) -> Simplygon.spComputeCaster:
"""Create compute caster for specified channel."""
print(f"Creating compute caster for {channel_name}")
caster = sg.CreateComputeCaster()
caster.SetOutputFilePath(output_path)
caster_settings = caster.GetComputeCasterSettings()
caster_settings.SetMaterialChannel(channel_name)
caster_settings.SetOutputColorSpace(color_space)
caster_settings.SetOutputPixelFormat(output_pixel_format)
caster_settings.SetOutputImageFileFormat( Simplygon.EImageOutputFormat_PNG )
caster_settings.SetDilation(dilation)
caster_settings.SetFillMode(fill_mode)
return caster
def billboard_asset(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, input_asset : str, asset_name : str):
"""Billboard the specified asset and use compute casters to transfer materials using serialized material description."""
# Load scene
print(f"Loading {input_asset}")
scene = load_scene(sg, input_asset)
# Load material description file
material_description_file = f"{INPUT_FOLDER}/{asset_name}.xml"
print(f"Load scene material description from {material_description_file}")
scene_description_serializer = sg.CreateMaterialEvaluationShaderSerializer()
scene_description_serializer.LoadSceneMaterialEvaluationShadersFromFile(material_description_file, scene)
# Create billboard pipeline
pipeline = create_billboard_pipeline(sg, 0.2, 0.7, 10, 2048)
# Add compute casters for all material channels
for channel in MATERIAL_CHANNELS:
compute_caster = create_compute_caster(sg, channel[0], channel[1], channel[2], channel[3], channel[4], f"{OUTPUT_TEXTURE_FOLDER}/{asset_name}_{channel[0]}" )
pipeline.AddMaterialCaster( compute_caster, 0 )
# Perform remeshing and material casting
print("Performing optimization...")
pipeline.RunScene(scene, Simplygon.EPipelineRunMode_RunInThisProcess)
# Check if we recieved any errors
print("Check log for any warnings or errors.")
check_log(sg)
# Since we output textures from material casters we clean texture table before saving the scenes.
# Otherwise we (depending on output file format) get the same texture twice on hard drive.
scene.GetTextureTable().Clear()
# Save scene
save_scene(sg, scene, f"{OUTPUT_FOLDER}/{asset_name}{FILE_ENDING}")
def check_log(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon):
"""Outputs any errors or warnings from Simplygon."""
# Check if any errors occurred.
has_errors = sg.ErrorOccurred()
if has_errors:
errors = sg.CreateStringArray()
sg.GetErrorMessages(errors)
error_count = errors.GetItemCount()
if error_count > 0:
print('CheckLog: Errors:')
for error_index in range(error_count):
error_message = errors.GetItem(error_index)
print(error_message)
sg.ClearErrorMessages()
else:
print('CheckLog: No errors.')
# Check if any warnings occurred.
has_warnings = sg.WarningOccurred()
if has_warnings:
warnings = sg.CreateStringArray()
sg.GetWarningMessages(warnings)
warning_count = warnings.GetItemCount()
if warning_count > 0:
print('CheckLog: Warnings:')
for warning_index in range(warning_count):
warning_message = warnings.GetItem(warning_index)
print(warning_message)
sg.ClearWarningMessages()
else:
print('CheckLog: No warnings.')
# Error out if Simplygon has errors.
if has_errors:
raise Exception('Processing failed with an error')
def process_asset(asset : str):
"""Initialize Simplygon and process asset."""
asset_name = asset.replace(FILE_ENDING, "")
sg = simplygon_loader.init_simplygon()
if sg is None:
exit(Simplygon.GetLastInitializationError())
billboard_asset(sg, f"{INPUT_FOLDER}/{asset}", asset_name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
for asset in os.listdir(INPUT_FOLDER):
if FILE_ENDING in asset:
process_asset(asset)
gc.collect()
fence_box.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Scene>
<TextureTable>
<Texture Name="modular_chainlink_fence_wire_diff_4k" FilePath="input/textures/modular_chainlink_fence_wire_diff_4k.png" ColorSpace="sRGB"/>
<Texture Name="modular_chainlink_fence_wire_rough_4k" FilePath="input/textures/modular_chainlink_fence_wire_rough_4k.png" ColorSpace="Linear"/>
<Texture Name="modular_chainlink_fence_wire_metal_4k" FilePath="input/textures/modular_chainlink_fence_wire_metal_4k.png" ColorSpace="Linear"/>
<Texture Name="modular_chainlink_fence_wire_nor_gl_4k" FilePath="input/textures/modular_chainlink_fence_wire_nor_gl_4k.png" ColorSpace="Linear"/>
<Texture Name="modular_chainlink_fence_posts_diff_4k" FilePath="input/textures/modular_chainlink_fence_posts_diff_4k.png" ColorSpace="sRGB"/>
<Texture Name="modular_chainlink_fence_posts_rough_4k" FilePath="input/textures/modular_chainlink_fence_posts_rough_4k.png" ColorSpace="Linear"/>
<Texture Name="modular_chainlink_fence_posts_metal_4k" FilePath="input/textures/modular_chainlink_fence_posts_metal_4k.png" ColorSpace="Linear"/>
<Texture Name="modular_chainlink_fence_posts_nor_gl_4k" FilePath="input/textures/modular_chainlink_fence_posts_nor_gl_4k.png" ColorSpace="Linear"/>
</TextureTable>
<MaterialTable>
<Material Name="modular_chainlink_fence_posts">
<MaterialEvaluationShader Version="0.4.0" ShaderLanguage="HLSL" ShaderFilePath="shaders/BasicMaterial.hlsl">
<Attribute Name="TexCoord" FieldType="TexCoords" FieldName="0" FieldFormat="F32vec2"/>
<Attribute Name="Tangent" FieldType="Tangents" FieldFormat="F32vec3"/>
<Attribute Name="Bitangent" FieldType="Bitangents" FieldFormat="F32vec3"/>
<Attribute Name="Normal" FieldType="Normals" FieldFormat="F32vec3"/>
<EvaluationFunction Channel="Diffuse" EntryPoint="CalculateDiffuseChannel"/>
<EvaluationFunction Channel="Metal" EntryPoint="CalculateMetalChannel"/>
<EvaluationFunction Channel="Roughness" EntryPoint="CalculateRoughnessChannel"/>
<EvaluationFunction Channel="Normals" EntryPoint="CalculateNormalsChannel"/>
<ShaderParameterSamplerState Name="Sampler2D" MinFilter="Linear" MagFilter="Linear" AddressU="Repeat" AddressV="Repeat" AddressW="Repeat" />
<ShaderParameterSampler Name="DiffuseTexture" SamplerState="Sampler2D" TextureName="modular_chainlink_fence_posts_diff_4k"/>
<ShaderParameterSampler Name="RoughnessTexture" SamplerState="Sampler2D" TextureName="modular_chainlink_fence_posts_rough_4k"/>
<ShaderParameterSampler Name="NormalTexture" SamplerState="Sampler2D" TextureName="modular_chainlink_fence_posts_nor_gl_4k"/>
<ShaderParameterSampler Name="MetalTexture" SamplerState="Sampler2D" TextureName="modular_chainlink_fence_posts_metal_4k"/>
</MaterialEvaluationShader>
</Material>
<Material Name="modular_chainlink_fence_wire">
<MaterialEvaluationShader Version="0.4.0" ShaderLanguage="HLSL" ShaderFilePath="shaders/AlphaCutoutMaterial.hlsl">
<Attribute Name="TexCoord" FieldType="TexCoords" FieldName="0" FieldFormat="F32vec2"/>
<Attribute Name="Tangent" FieldType="Tangents" FieldFormat="F32vec3"/>
<Attribute Name="Bitangent" FieldType="Bitangents" FieldFormat="F32vec3"/>
<Attribute Name="Normal" FieldType="Normals" FieldFormat="F32vec3"/>
<EvaluationFunction Channel="Diffuse" EntryPoint="CalculateDiffuseChannel"/>
<EvaluationFunction Channel="Metal" EntryPoint="CalculateMetalChannel"/>
<EvaluationFunction Channel="Roughness" EntryPoint="CalculateRoughnessChannel"/>
<EvaluationFunction Channel="Normals" EntryPoint="CalculateNormalsChannel"/>
<ShaderParameterSamplerState Name="Sampler2D" MinFilter="Linear" MagFilter="Linear" AddressU="Repeat" AddressV="Repeat" AddressW="Repeat" />
<ShaderParameterSampler Name="DiffuseTexture" SamplerState="Sampler2D" TextureName="modular_chainlink_fence_wire_diff_4k"/>
<ShaderParameterSampler Name="RoughnessTexture" SamplerState="Sampler2D" TextureName="modular_chainlink_fence_wire_rough_4k"/>
<ShaderParameterSampler Name="NormalTexture" SamplerState="Sampler2D" TextureName="modular_chainlink_fence_wire_nor_gl_4k"/>
<ShaderParameterSampler Name="MetalTexture" SamplerState="Sampler2D" TextureName="modular_chainlink_fence_wire_metal_4k"/>
</MaterialEvaluationShader>
</Material>
</MaterialTable>
</Scene>
AlphaCutoutMaterial.hlsl
// Sample Diffuse texture for diffuse channel
float4 CalculateDiffuseChannel()
{
float4 color = DiffuseTexture.SampleLevel(DiffuseTextureSamplerState, TexCoord,0);
// If we have alpha less then cutoff value discard this value and instead use previous value.
if (color.a <= 0.5f) {
sg_DiscardValue = true;
return sg_PreviousValue;
}
return color;
}
// Sample Metal texture
float4 CalculateMetalChannel()
{
// If we have alpha less then cutoff value discard this value and instead use previous value.
// Notice that we check the diffuse texture's alpha, not metal channel.
float4 color = DiffuseTexture.SampleLevel(DiffuseTextureSamplerState, TexCoord,0);
if (color.a <= 0.5f) {
sg_DiscardValue = true;
return sg_PreviousValue;
}
float4 metal = MetalTexture.SampleLevel(MetalTextureSamplerState, TexCoord,0);
return metal;
}
// Sample Roughness texture
float4 CalculateRoughnessChannel()
{
// If we have alpha less then cutoff value discard this value and instead use previous value.
// Notice that we check the diffuse texture's alpha.
float4 color = DiffuseTexture.SampleLevel(DiffuseTextureSamplerState, TexCoord,0);
if (color.a <= 0.5f) {
sg_DiscardValue = true;
return sg_PreviousValue;
}
float4 roughness = RoughnessTexture.SampleLevel(RoughnessTextureSamplerState, TexCoord,0);
return roughness;
}
// The CalculateNormalsChannel calculates the per-texel normals of the output tangent-space normal map. It starts by sampling the input
// tangent-space normal map of the input geometry, and transforms the normal into object-space coordinates. It then uses the generated
// destination tangent basis vectors to transform the normal vector into the output tangent-space.
float4 CalculateNormalsChannel()
{
// If we have alpha less then cutoff value discard this value and instead use previous value.
// Notice that we check the diffuse texture's alpha.
float4 color = DiffuseTexture.SampleLevel(DiffuseTextureSamplerState, TexCoord,0);
if (color.a <= 0.5f) {
sg_DiscardValue = true;
return sg_PreviousValue;
}
float3 tangentSpaceNormal = (NormalTexture.SampleLevel(NormalTextureSamplerState, TexCoord,0).xyz * 2.0) - 1.0;
// transform into an object-space vector
float3 objectSpaceNormal = tangentSpaceNormal.x * normalize(Tangent) +
tangentSpaceNormal.y * normalize(Bitangent) +
tangentSpaceNormal.z * normalize(Normal);
// transform the object-space vector into the destination tangent space
tangentSpaceNormal.x = dot( objectSpaceNormal , normalize(sg_DestinationTangent) );
tangentSpaceNormal.y = dot( objectSpaceNormal , normalize(sg_DestinationBitangent) );
tangentSpaceNormal.z = dot( objectSpaceNormal , normalize(sg_DestinationNormal) );
// normalize, the tangent basis is not necessarily orthogonal
tangentSpaceNormal = normalize(tangentSpaceNormal);
// encode into [0 -> 1] basis and return
return float4( ((tangentSpaceNormal + 1.0)/2.0) , 1.0);
}
BasicMaterial.hlsl
// Sample Diffuse texture for diffuse channel
float4 CalculateDiffuseChannel()
{
float4 color = DiffuseTexture.SampleLevel(DiffuseTextureSamplerState, TexCoord,0);
return color;
}
// Sample Roughness texture for roughness channel
float4 CalculateRoughnessChannel()
{
float4 color = RoughnessTexture.SampleLevel(RoughnessTextureSamplerState, TexCoord,0);
return color;
}
// Sample metal texture
float4 CalculateMetalChannel()
{
float4 color = MetalTexture.SampleLevel(MetalTextureSamplerState, TexCoord,0);
return color;
}
// The CalculateNormalsChannel calculates the per-texel normals of the output tangent-space normal map. It starts by sampling the input
// tangent-space normal map of the input geometry, and transforms the normal into object-space coordinates. It then uses the generated
// destination tangent basis vectors to transform the normal vector into the output tangent-space.
float4 CalculateNormalsChannel()
{
float3 tangentSpaceNormal = (NormalTexture.SampleLevel(NormalTextureSamplerState, TexCoord,0).xyz * 2.0) - 1.0;
// transform into an object-space vector
float3 objectSpaceNormal = tangentSpaceNormal.x * normalize(Tangent) +
tangentSpaceNormal.y * normalize(Bitangent) +
tangentSpaceNormal.z * normalize(Normal);
// transform the object-space vector into the destination tangent space
tangentSpaceNormal.x = dot( objectSpaceNormal , normalize(sg_DestinationTangent) );
tangentSpaceNormal.y = dot( objectSpaceNormal , normalize(sg_DestinationBitangent) );
tangentSpaceNormal.z = dot( objectSpaceNormal , normalize(sg_DestinationNormal) );
// normalize, the tangent basis is not necessarily orthogonal
tangentSpaceNormal = normalize(tangentSpaceNormal);
// encode into [0 -> 1] basis and return
return float4( ((tangentSpaceNormal + 1.0)/2.0) , 1.0);
}
