Load additional texture channels into a Simplygon scene

Written by Jesper Tingvall, Product Expert, Simplygon
Disclaimer: The code in this post is written using version 10.4.272.0 of Simplygon. If you encounter this post at a later stage, some of the API calls might have changed. However, the core concepts should still remain valid.
Introduction
In this blog post, we will showcase how to load textures into additional material channels in a file. This is useful if you are using material channels not defined in a standard file format (like FBX).
Prerequisites
This example will use the Simplygon Python API, but the same concepts can be applied to all other integrations of the Simplygon API.
Problem to solve
We have a chair FBX model that we want to optimize with a material casting-based pipeline, in our case remeshing. The model has been adapted to suit the topic of the blog better.
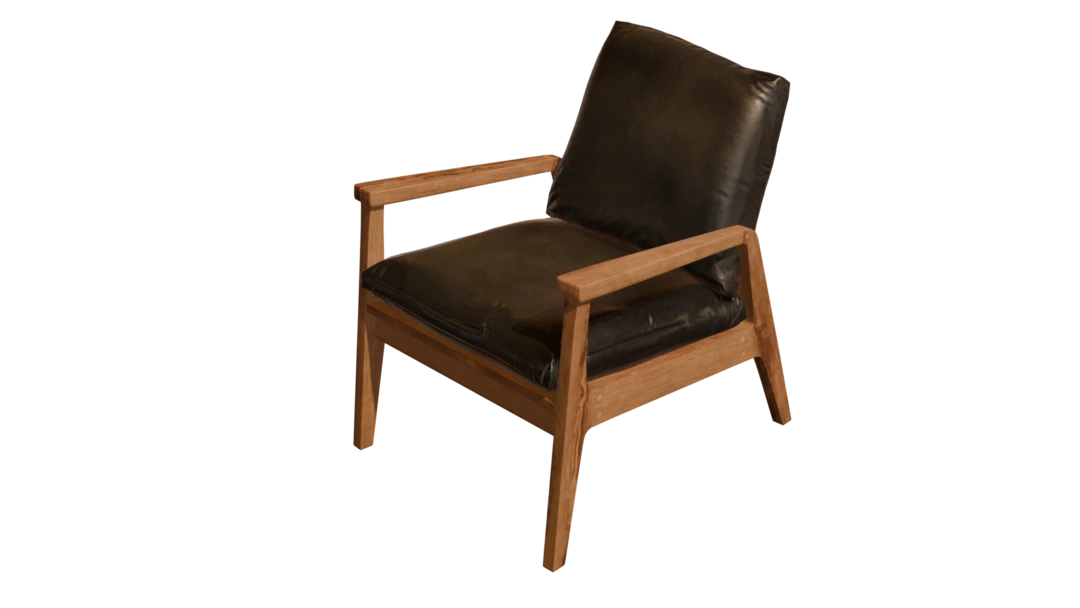

The asset uses 3 textures:
- Diffuse
- Roughness
- Normal
If we try to process the asset using the API directly, we can cast diffuse and normal textures, but not roughness.
We want to process not just one file, but an entire folder of models and textures. The files are structured in folders like this:
Input/
|--> modern_arm_chair_01_4k.fbx/
| |--> textures
| | |--> modern_arm_chair_01_legs_Diffuse.png
| | |--> modern_arm_chair_01_legs_Normal.png
| | |--> modern_arm_chair_01_legs_Roughness.png
| | |--> modern_arm_chair_01_pillow_Diffuse.png
| | |--> modern_arm_chair_01_pillow_Normal.png
| | |--> modern_arm_chair_01_pillow_Roughness.png
| |--> modern_arm_chair_01_4k.fbx
|--> yet_another_chair.fbx/
| |--> textures
| | |--> more_legs_Diffuse.png
| | |--> more_legs_Normal.png
| | |--> more_legs_Roughness.png
| | |--> ...
| |--> yet_another_chair.fbx
|--> ...
inject_texture.py
Solution
We are going to create a batch processor which takes a folder structure and processes all assets in it. It will have the capability of loading additional textures not defined in our model format and casting these as well.
Textures, materials and channels
Let us start by explaining some concepts that we are going to use later in this blog.
- A Simplygon scene contains one or several Materials. These are referenced by geometry data by ID.
- Materials have one or several Material Channels, like albedo, roughness, normals. A material channel references a shading network which describes what the material's surfaces are and is used by Simplygon's material casters.
- A Simplygon scene contains a texture table containing Textures. These are referenced by name by shading networks.
We will first look at what channels that are defined in our fbx file. We can do this with this code snipped which iterates through all materials in the file and print all channels it has.
def print_texture_channels(scene: Simplygon.spScene) -> None:
"""Print all materials and their channels in a scene."""
material_table = scene.GetMaterialTable()
for i in range(0, material_table.GetMaterialsCount()):
material = material_table.GetMaterial(i)
print(f"{material.GetName()} material channels:")
for j in range(0, material.GetMaterialChannelCount()):
print(f" - {material.GetMaterialChannelFromIndex(j)}")
Here are all materials defined in our fbx file. We are lacking a channel roughness channel preventing us from being able to cast that texture.
modern_arm_chair_01_legs material channels:
- Diffuse
- Normals
modern_arm_chair_01_pillow material channels:
- Diffuse
- Normals
Import texture into scene
First step is to import the roughness texture into our Simplygon scene. Importing of images is handled via ImageDataImporter. It is then used to create a Texture that is added to the scene's texture table. We can then refer to the texture via the name given by SetName.
def import_texture_into_scene(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, scene: Simplygon.spScene, texture_name: str, texture_path: str) -> None:
"""Import texture and add to scene's texture table."""
importer = sg.CreateImageDataImporter()
importer.SetImportFilePath(texture_path)
success = importer.RunImport()
if (not success):
raise Exception(f"Failed to load {texture_path}")
texture = sg.CreateTexture()
texture.SetName(texture_name)
texture.SetImageData(importer.GetImage())
scene.GetTextureTable().AddTexture(texture)
Create simple shading network
To make the texture accessible for material casters we need to reference it via a shading network. Our shading network consists of only one ShadingTextureNode. It's TextureName is set to the name of our newly imported texture.
def create_shading_network(sg : Simplygon.ISimplygon, textureName: str) -> None:
"""Create simple shading network with texture node to references texture."""
texture_node = sg.CreateShadingTextureNode()
texture_node.SetTextureName(textureName)
texture_node.SetTexCoordLevel(0)
# Set color space to undefined, so Simplygon will use the one from the imported image.
texture_node.SetColorSpaceOverride(Simplygon.EImageColorSpace_Undefined)
return texture_node
Add additional material channels
Using the two helper functions we created above we can now load textures in additional material channels. To keep this example simple our textures are named [material_name]_[channel_name].png. A better way of doing this would be to have a metadata file alongside the model that describes what textures should be loaded in.
We iterate through our material table, then for every material we load in the additional texture, create a shading network for it and add that as a material channel.
def load_additional_textures(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, scene: Simplygon.spScene, texture_folder: str, material_channel: str) -> None:
"""Load texture file into a material channel."""
material_table = scene.GetMaterialTable()
for i in range(0, material_table.GetMaterialsCount()):
material = material_table.GetMaterial(i)
material_name = material.GetName()
texture_name = f"{material_name}_{material_channel}"
texture_path = f"{texture_folder}/{texture_name}.png"
import_texture_into_scene(sg, scene, texture_name, texture_path)
textureShadingNetwork = create_shading_network(sg, texture_name)
material.AddMaterialChannel(material_channel)
material.SetShadingNetwork(material_channel, textureShadingNetwork)
Add casters
Let us now add casters for all material channels. This function will create a color caster and set its material channel and color space.
def add_color_caster(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, pipeline: Simplygon.spPipeline, material_channel: str, is_srgb: bool, output_file: str) -> None:
"""Create a color caster for specified channel."""
caster = sg.CreateColorCaster()
caster_settings = caster.GetColorCasterSettings()
caster_settings.SetMaterialChannel(material_channel)
caster_settings.SetOutputSRGB(is_srgb)
caster.SetOutputFilePath(output_file)
pipeline.AddMaterialCaster( caster, 0 )
For casting normals we need to use a specific kind of caster, a normal caster. Notice that we do not set color space, normal maps should always use linear color space.
def add_normal_caster(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, pipeline: Simplygon.spPipeline, material_channel: str, output_file: str) -> None:
"""Create a normal caster for specified channel."""
caster = sg.CreateNormalCaster()
caster_settings = caster.GetNormalCasterSettings()
caster_settings.SetGenerateTangentSpaceNormals(True)
caster_settings.SetMaterialChannel(material_channel)
caster.SetOutputFilePath(output_file)
pipeline.AddMaterialCaster( caster, 0 )
Our asset has 3 channels, here we create casters corresponding to each one of them.
- Diffuse saved in sRGB color space.
- Roughness saved in linear color space.
- Normals saved in linear color space.
add_color_caster(sg, pipeline, "Diffuse", True, f"{output_texture_folder}/Diffuse.png")
add_color_caster(sg, pipeline, "Roughness", True, f"{output_texture_folder}/Roughness.png")
add_normal_caster(sg, pipeline, "Normals", f"{output_texture_folder}/Normals.png")
After casting we get our 3 output textures. We can see that the two materials we had in our scene, wooden legs and pillow are both merged into the texture atlas.
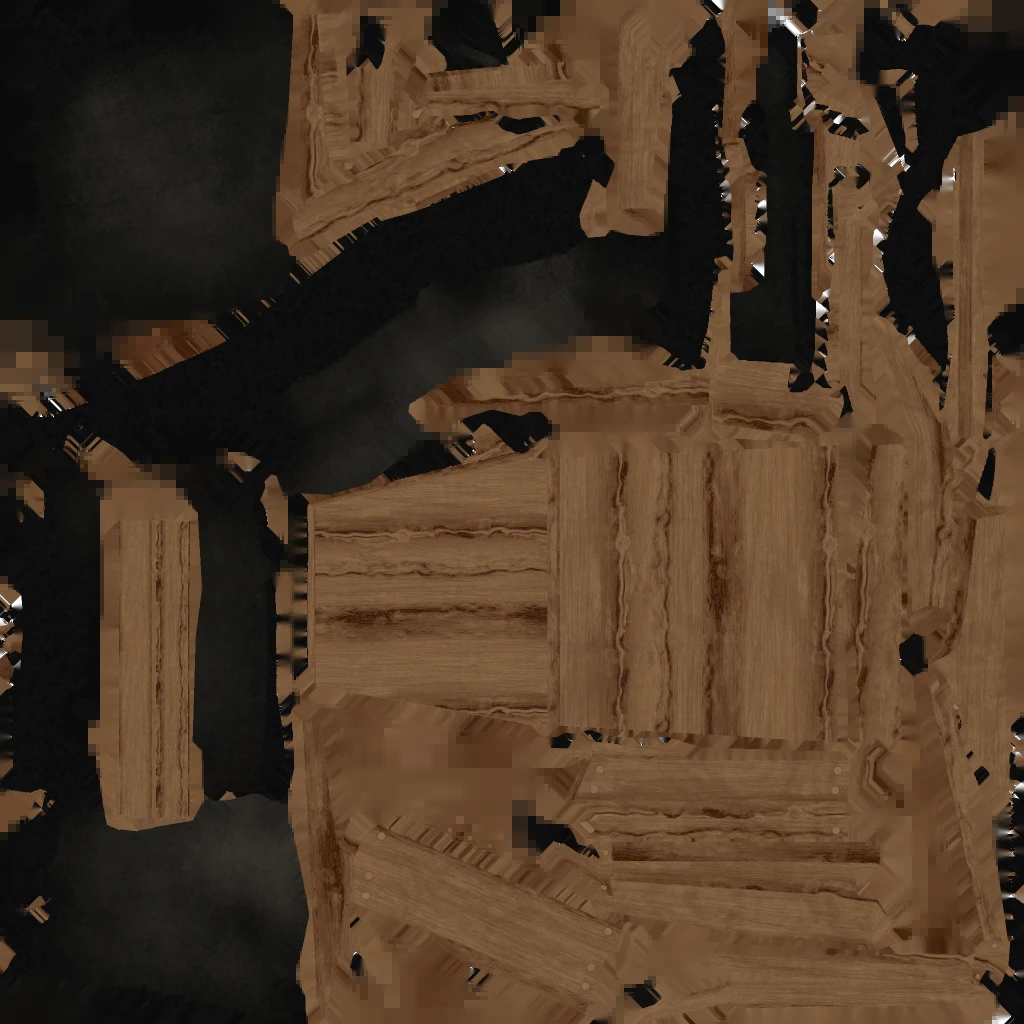


If you discover that the color is off for one of the output textures it is very likely that gamma (sRGB) is the issue. Consult this blog on troubleshooting gamma issues for more information.
Result
We can now optimize our model and cast all required texture channels. We can easily extend this script if our material model requires additional texture channels that are not defined in any model format.

| Model | Triangle count | Material count | Texture references |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 9 k | 2 | 6 x 4k textures |
| Remeshed proxy | 1 k | 1 | 3 x 1k textures |
Complete scripts
# Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.
# Licensed under the MIT license.
from simplygon10 import simplygon_loader
from simplygon10 import Simplygon
import os
def process_asset(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, asset: str, texture_folder: str, output_model: str, output_texture_folder: str) -> None:
print("Optimizing " + asset)
importer = sg.CreateSceneImporter()
importer.SetImportFilePath(asset)
if importer.Run() == Simplygon.EErrorCodes_NoError:
scene = importer.GetScene()
# Print which texture channels we have in our scene
# print_texture_channels(scene)
# Load Roughness channel into our scene
load_additional_textures(sg, scene, texture_folder, "Roughness")
# Create remeshing pipeline and material casters
pipeline = create_remeshing_pipeline_screen_size(sg, 300, 1024)
add_color_caster(sg, pipeline, "Diffuse", True, f"{output_texture_folder}/Diffuse.png")
add_color_caster(sg, pipeline, "Roughness", False, f"{output_texture_folder}/Roughness.png")
add_normal_caster(sg, pipeline, "Normals", f"{output_texture_folder}/Normals.png")
pipeline.RunScene(scene, Simplygon.EPipelineRunMode_RunInThisProcess)
# Since we output textures from material casters we clean texture table before saving the scenes.
# Otherwise we (depending on output file format) get the same texture twice on hard drive.
scene.GetTextureTable().Clear()
export_output(sg, scene, output_model)
else:
print("Error: Failed to import " + asset)
def print_texture_channels(scene: Simplygon.spScene) -> None:
"""Print all materials and their channels in a scene."""
material_table = scene.GetMaterialTable()
for i in range(0, material_table.GetMaterialsCount()):
material = material_table.GetMaterial(i)
print(f"{material.GetName()} material channels:")
for j in range(0, material.GetMaterialChannelCount()):
print(f" - {material.GetMaterialChannelFromIndex(j)}")
def load_additional_textures(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, scene: Simplygon.spScene, texture_folder: str, material_channel: str) -> None:
"""Load texture file into a material channel."""
material_table = scene.GetMaterialTable()
for i in range(0, material_table.GetMaterialsCount()):
material = material_table.GetMaterial(i)
material_name = material.GetName()
texture_name = f"{material_name}_{material_channel}"
texture_path = f"{texture_folder}/{texture_name}.png"
import_texture_into_scene(sg, scene, texture_name, texture_path)
textureShadingNetwork = create_shading_network(sg, texture_name)
material.AddMaterialChannel(material_channel)
material.SetShadingNetwork(material_channel, textureShadingNetwork)
def create_shading_network(sg : Simplygon.ISimplygon, textureName: str) -> None:
"""Create simple shading network with texture node to references texture."""
texture_node = sg.CreateShadingTextureNode()
texture_node.SetTextureName(textureName)
texture_node.SetTexCoordLevel(0)
# Set color space to undefined, so Simplygon will use the one from the imported image.
texture_node.SetColorSpaceOverride(Simplygon.EImageColorSpace_Undefined)
return texture_node
def import_texture_into_scene(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, scene: Simplygon.spScene, texture_name: str, texture_path: str) -> None:
"""Import texture and add to scene's texture table."""
importer = sg.CreateImageDataImporter()
importer.SetImportFilePath(texture_path)
success = importer.RunImport()
if (not success):
raise Exception(f"Failed to load {texture_path}")
texture = sg.CreateTexture()
texture.SetName(texture_name)
texture.SetImageData(importer.GetImage())
scene.GetTextureTable().AddTexture(texture)
def create_remeshing_pipeline_screen_size(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, screen_size: int, texture_size: int) -> None:
"""Create remeshing pipelie for given screen size and texture size."""
sgRemeshingProcessor = sg.CreateRemeshingPipeline()
sgRemeshingSettings = sgRemeshingProcessor.GetRemeshingSettings()
mapping_image_settings = sgRemeshingProcessor.GetMappingImageSettings()
material_output_settings = mapping_image_settings.GetOutputMaterialSettings(0)
# Set quality of material casting.
material_output_settings.SetTextureHeight(texture_size)
material_output_settings.SetTextureWidth(texture_size)
mapping_image_settings.SetGenerateMappingImage(True)
mapping_image_settings.SetTexCoordName("MaterialLOD")
# Set quality of remeshing.
sgRemeshingSettings.SetOnScreenSize( screen_size )
return sgRemeshingProcessor
def add_color_caster(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, pipeline: Simplygon.spPipeline, material_channel: str, is_srgb: bool, output_file: str) -> None:
"""Create a color caster for specified channel."""
caster = sg.CreateColorCaster()
caster_settings = caster.GetColorCasterSettings()
caster_settings.SetMaterialChannel(material_channel)
caster_settings.SetOutputSRGB(is_srgb)
caster.SetOutputFilePath(output_file)
pipeline.AddMaterialCaster( caster, 0 )
def add_normal_caster(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, pipeline: Simplygon.spPipeline, material_channel: str, output_file: str) -> None:
"""Create a normal caster for specified channel."""
caster = sg.CreateNormalCaster()
caster_settings = caster.GetNormalCasterSettings()
caster_settings.SetGenerateTangentSpaceNormals(True)
caster_settings.SetMaterialChannel(material_channel)
caster.SetOutputFilePath(output_file)
pipeline.AddMaterialCaster( caster, 0 )
def process_assets(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, input_dir: str, output_dir : str) -> None:
"""Process all assets in folder."""
for asset_folder in os.listdir(input_dir):
for model in os.listdir(f"{input_dir}/{asset_folder}"):
if ".fbx" in model:
process_asset(sg, f"{input_dir}/{asset_folder}/{model}", f"{input_dir}/{asset_folder}/textures", f"{output_dir}/{asset_folder}/{model}", f"{output_dir}/{asset_folder}/textures")
def export_output(sg: Simplygon.ISimplygon, scene: Simplygon.spScene, path:str) -> None:
"""Export scene to file."""
exporter = sg.CreateSceneExporter()
exporter.SetScene(scene)
print("Saving " + path)
exporter.SetExportFilePath( path )
exporter.Run()
def main() -> None:
print("Starting batch processing")
sg = simplygon_loader.init_simplygon()
process_assets(sg, "Input", "Output")
if __name__== "__main__":
main()
