Bake vertex colors into textures
Written by Jesper Tingvall, Product Expert, Simplygon
Disclaimer: The code in this post is written using version 10.1.8000.0 of Simplygon and Blender 3.1.2. If you encounter this post at a later stage, some of the API calls might have changed. However, the core concepts should still remain valid.
Introduction
In this blog we'll look at how to bake vertex colors into textures. Use case for this is certain photo scanned assets where color data is saved into vertex colors. We'll look at how to do this with both the remesher and aggregator pipeline. We'll also cover how to create a shading network for vertex colored materials as well as how to remove vertex colors from model post processing.
This blog is more or less the inverse of our Bake textures into vertex colors blog in which we go other way around; texture to vertex colors.

Prerequisites
This example will use the Simplygon integration in Blender, but the same concepts can be applied to all other integrations of the Simplygon API.
Problem to solve
The asset we want to optimize is a photo scanned asset without UVs where the color data is saved as vertex colors. Our desired output is a model where color data is kept in a texture. The input asset is very dense so we would want to make it more lightweight.
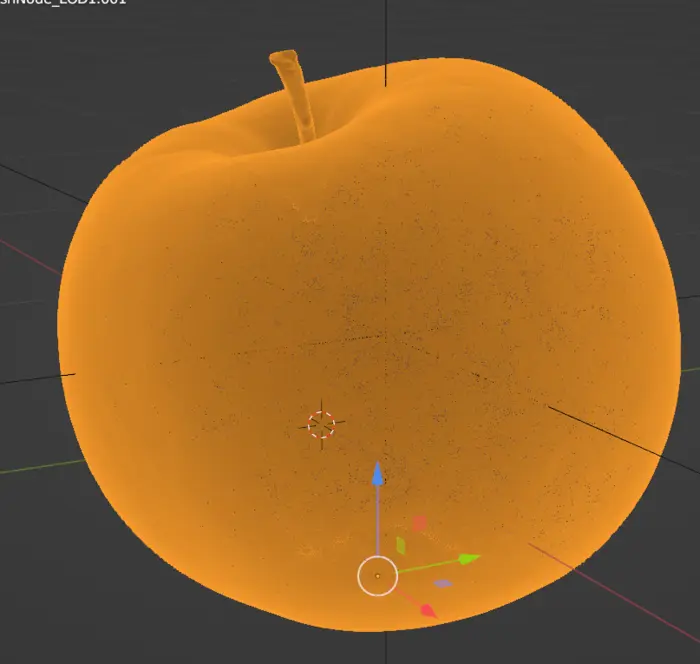
Solution using remeshing
As our original model has very dense geometry it is likely we want to get it down in poly count as well. Our remeshing pipeline is perfect for this task.
Export from Blender
First step is to export from Blender into Simplygon. To do this we are going to export the scene as glTF then import it into Simplygon using a scene importer.
def export_selection(sg, file_path):
"""Export the current selected objects into Simplygon."""
bpy.ops.export_scene.gltf(filepath = file_path, use_selection=True)
sceneImporter = sg.CreateSceneImporter()
sceneImporter.SetImportFilePath(file_path)
sceneImporter.Run()
scene = sceneImporter.GetScene()
return scene
Set up vertex color shading network
If we would perform color caster against the asset via UI we would not get any color output. Reason for that is that the color is stored in vertex color rather then in a texture. To make the color caster understand we want to use vertex color as input we need to create a custom shading network.
First we need to add a material channel for our base color. In Blender this is named Basecolor. We can then create a vertex color node and specify which VertexColorIndex to use. In our case we only have one vertex color so index is 0. We then assign our vertex color node as the shading network for our material's color channel.
def setup_vertex_color_material(sg, material, channel):
"""Set material to use vertex color as color."""
material.AddMaterialChannel(channel)
shading_node = sg.CreateShadingVertexColorNode()
shading_node.SetVertexColorIndex(vertex_color_index)
material.SetShadingNetwork(channel, shading_node)
Once we have a function for creating a vertex colored material we can iterate through every material in the scene's material table and set it up to use our custom vertex color shaded network.
def setup_vertex_color_materials(sg, scene):
"""Set all materials in scene to vertex colored."""
material_table = scene.GetMaterialTable()
for i in range(0, material_table.GetMaterialsCount()):
material = material_table.GetMaterial(i)
setup_vertex_color_material(sg, material, color_channel)
Create remeshing pipeline
Our remeshing pipeline does two things; creates a watertight low poly mesh and bakes materials from original asset to it. This makes it perfect for our use case. We start by creating a remesh pipeline then setting OnScreenSize according to our desired model output quality. It is worth to mention that very high on screen size makes it scale poorly, in those cases have a look at our blog Accelerated remeshing using tessellated attributes on how to speed it up.
The mapping image is responsible for translating surface from the original model to our remeshed one. We need to create one in order to transfer material, so GenerateMappingImage needs to be set to True. We can also specify size using TextureHeight and TextureWidth.
def create_pipline(sg):
"""Create remesing pipeline and color caster."""
pipeline = sg.CreateRemeshingPipeline()
settings = pipeline.GetRemeshingSettings()
settings.SetOnScreenSize(resolution)
mapping_image_settings = pipeline.GetMappingImageSettings()
material_output_settings = mapping_image_settings.GetOutputMaterialSettings(0)
material_output_settings.SetTextureHeight(texture_size)
material_output_settings.SetTextureWidth(texture_size)
mapping_image_settings.SetGenerateMappingImage(True)
mapping_image_settings.SetTexCoordName("MaterialLOD")
To being able to bake the color we add a color caster to our remeshing pipeline. It will be automatically be cast when we run the pipeline. What we need to specify is what MaterialChannel to bake, this should be same as what our vertex colored material outputs - Basecolor.
caster = sg.CreateColorCaster()
caster_settings = caster.GetColorCasterSettings()
caster_settings.SetMaterialChannel( color_channel )
pipeline.AddMaterialCaster( caster, 0 )
return pipeline
Import into Blender
To get the result back into Blender we are going to use a scene exporter to export our optimized scene as a gltf file. We can then then import into Blender.
def import_results(sg, scene, file_path):
"""Import the Simplygon scene into Blender."""
scene_exporter = sg.CreateSceneExporter()
scene_exporter.SetExportFilePath(file_path)
scene_exporter.SetScene(scene)
scene_exporter.Run()
bpy.ops.import_scene.gltf(filepath=file_path)
Putting it all together
Once all helper functions are created we can put it all together. First we are going to export the selected mesh from Blender, then setup our custom vertex colored material. After that we create a remeshing pipeline and run it. Lastly we import the result back into Blender.
def process_selection(sg):
"""Process selected mesh in Blender"""
# Export scene from Blender and import it
file_path = temp_path + file
scene = export_selection(sg, file_path)
# Setup vertex color shader
setup_vertex_color_materials(sg, scene)
# Process scene
pipeline = create_pipline(sg)
pipeline.RunScene(scene, Simplygon.EPipelineRunMode_RunInThisProcess)
# Import result into Blender
import_results(sg, scene, file_path)
Remeshing result
The end result is a low poly model where the vertex colors are baked into a texture. Perfect to use for runtime visualization.
| Asset | Triangles |
|---|---|
| Original asset | 673 152 |
| Optimized asset | 988 |

And all vertex colors are now baked into a texture.
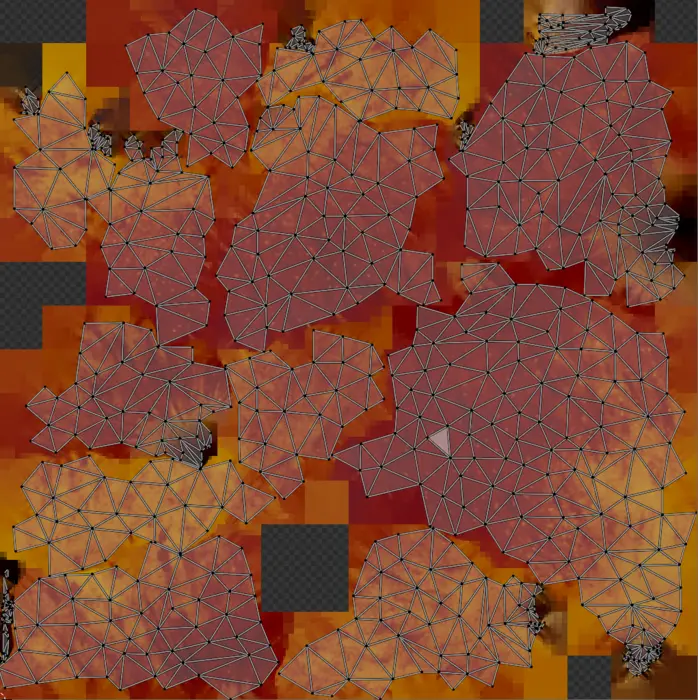
One thing which would improve our result further would be to add a normal caster as well that can transfer any tiny geometric details into a normal map.
Aggregation solution
If we want to keep the geometry intact but just bake a UV map we can use aggregation pipeline instead of remeshing. Many parts of of the code are identical so we will just go into the new parts.
Remove vertex colors
Since our color data now resides in a texture we can remove the vertex color field from the scene. To do this we first find all meshes in the scene by creating a selection set containing all SceneMesh nodes. After that we iterate over them one by one.
def remove_vertex_weights(sg, scene, vertex_color_index):
"""Remove all vertex colors of index from scene."""
scene_meshes_selection_set_id = scene.SelectNodes("SceneMesh")
scene_meshes_selection_set = scene.GetSelectionSetTable().GetSelectionSet(scene_meshes_selection_set_id)
# Loop through all meshes in the scene
for node_id in range(scene_meshes_selection_set.GetItemCount()):
After SafeCasting the node to SceneMesh we can get out the geometry data from it. Here we can manipulate it, in our case we will remove the vertex color field by calling RemoveColors. In our Blender asset this was vertex color index 0.
scene_mesh = Simplygon.spSceneMesh.SafeCast(scene.GetNodeByGUID( scene_meshes_selection_set.GetItem(node_id)))
# Get geometry for mesh
geometry = scene_mesh.GetGeometry()
if not geometry:
continue
geometry.RemoveColors(vertex_color_index)
The above function can be useful for cleaning up assets post optimization if you have vertex colors in them only used for guiding Simplygon using vertex weights. The function could then be called after optimization.
Create aggregation pipeline
Since we want to keep the mesh intact we instead use the aggregation pipeline for processing the mesh. As above we need to create a mapping image which we will use to transfer from vertex colors to texture. With TexCoordGeneratorType set to ETexcoordGeneratorType_Parameterizer we use our parameterizer in Simplygon to create a new UV map for our asset.
def create_aggregaton_pipline(sg):
"""Create aggregation pipeline with color material caster"""
aggregation_pipeline = sg.CreateAggregationPipeline()
aggregator_settings = aggregation_pipeline.GetAggregationSettings()
mapping_image_settings = aggregation_pipeline.GetMappingImageSettings()
mapping_image_settings.SetGenerateMappingImage(True)
material_settings = mapping_image_settings.GetOutputMaterialSettings(0)
material_settings.SetTextureWidth(texture_size)
material_settings.SetTextureHeight(texture_size)
mapping_image_settings.SetTexCoordGeneratorType( Simplygon.ETexcoordGeneratorType_Parameterizer )
We then add a color caster in exactly the same way as our remeshing pipeline.
caster = sg.CreateColorCaster()
caster_settings = caster.GetColorCasterSettings()
caster_settings.SetMaterialChannel( color_channel )
aggregation_pipeline.AddMaterialCaster( caster, 0 )
return aggregation_pipeline
Putting it all together
The only difference from remeshing solution is that we call remove_vertex_weights after running our pipeline.
def process_selection(sg):
"""Remove and bake decals on selected meshes."""
# Export scene from Blender and import it
file_path = temp_path + file
scene = export_selection(sg, file_path)
# Setup vertex color shader
setup_vertex_color_materials(sg, scene)
# Aggregate optimized scene
pipeline = create_aggregaton_pipline(sg)
pipeline.RunScene(scene, Simplygon.EPipelineRunMode_RunInThisProcess)
# Clean up vertex colors
remove_vertex_weights(sg, scene, vertex_color_index)
# Import result into Blender
import_results(sg, scene, file_path)
Aggregation result
The result after running the aggregation script is a model where the mesh is kept intact.
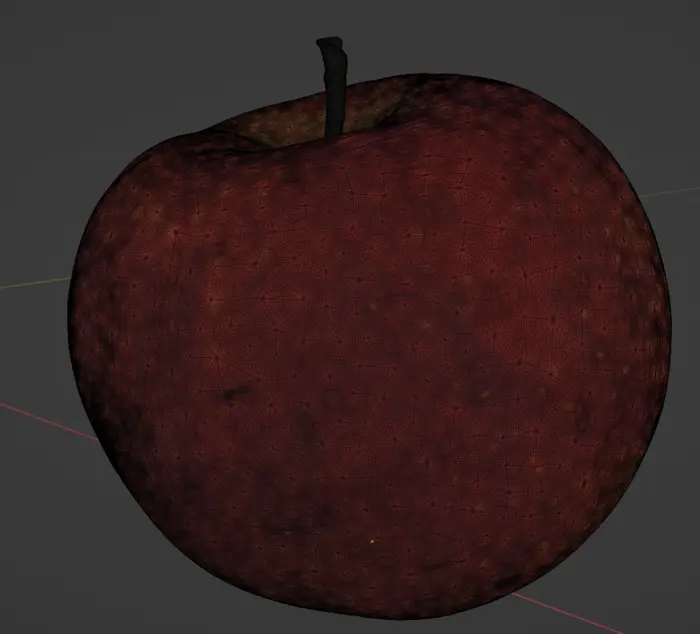

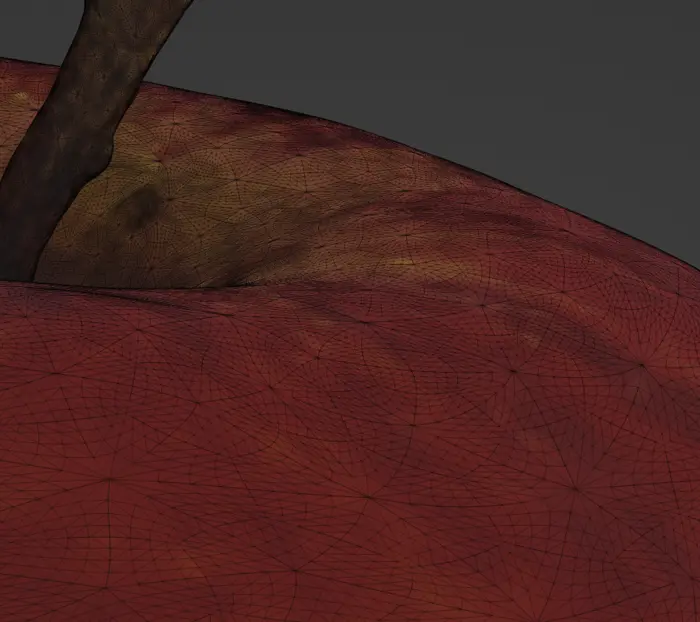
We have removed the vertex color field from it and color is instead saved in a texture and we use a freshly baked UV map to access it. Black part of image is the very dense UV map.
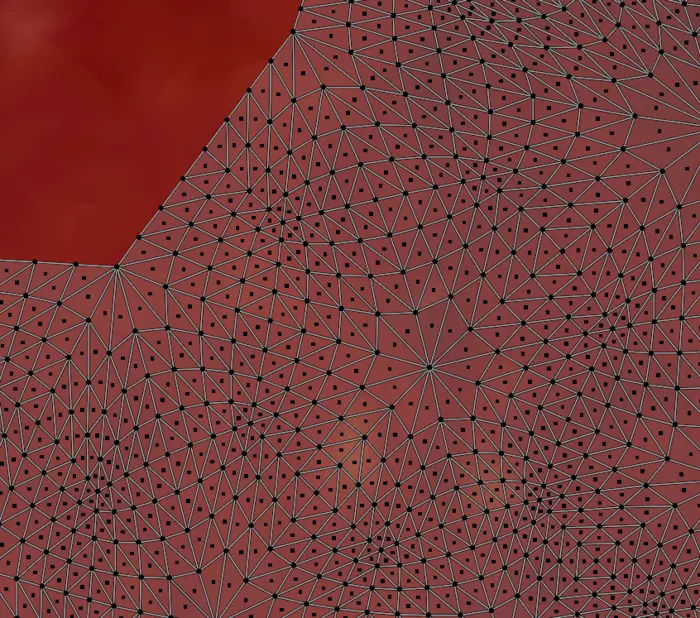
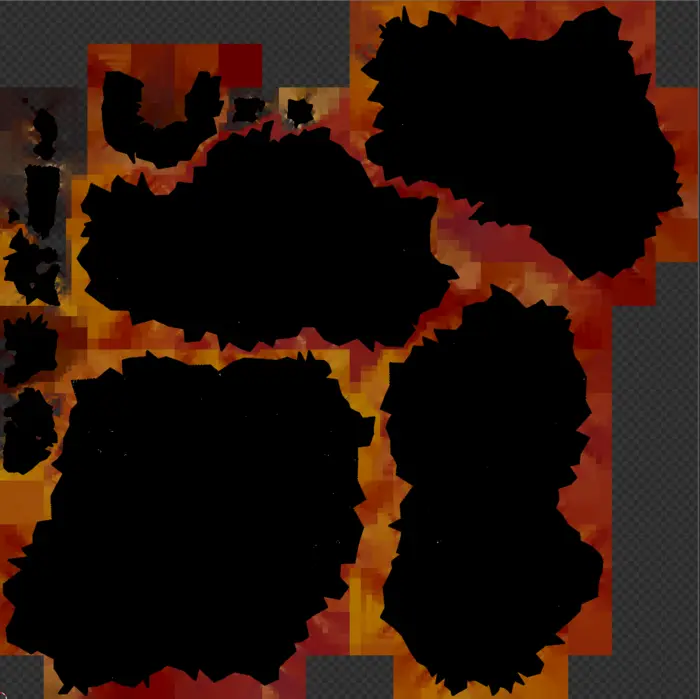

The use case for this is probably quite narrow, but we wanted to include it as it also covered how to remove vertex colors from a mesh post optimization, a code snippet that could be useful.
Complete scripts
Remeshing
# Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.
# Licensed under the MIT license.
import os
import bpy
import gc
from simplygon10 import simplygon_loader
from simplygon10 import Simplygon
file = "scene.glb"
temp_path = "c:/tmp/"
# Change parameters for quality
texture_size = 4096
resolution = 300
# Blender specific settings
color_channel = "Basecolor"
vertex_color_index = 0
def export_selection(sg, file_path):
"""Export the current selected objects into Simplygon."""
bpy.ops.export_scene.gltf(filepath = file_path, use_selection=True)
sceneImporter = sg.CreateSceneImporter()
sceneImporter.SetImportFilePath(file_path)
sceneImporter.Run()
scene = sceneImporter.GetScene()
return scene
def import_results(sg, scene, file_path):
"""Import the Simplygon scene into Blender."""
scene_exporter = sg.CreateSceneExporter()
scene_exporter.SetExportFilePath(file_path)
scene_exporter.SetScene(scene)
scene_exporter.Run()
bpy.ops.import_scene.gltf(filepath=file_path)
def create_pipline(sg):
"""Create remesing pipeline and color caster."""
pipeline = sg.CreateRemeshingPipeline()
settings = pipeline.GetRemeshingSettings()
settings.SetOnScreenSize(resolution)
mapping_image_settings = pipeline.GetMappingImageSettings()
material_output_settings = mapping_image_settings.GetOutputMaterialSettings(0)
material_output_settings.SetTextureHeight(texture_size)
material_output_settings.SetTextureWidth(texture_size)
mapping_image_settings.SetGenerateMappingImage(True)
mapping_image_settings.SetTexCoordName("MaterialLOD")
caster = sg.CreateColorCaster()
caster_settings = caster.GetColorCasterSettings()
caster_settings.SetMaterialChannel( color_channel )
pipeline.AddMaterialCaster( caster, 0 )
return pipeline
def setup_vertex_color_materials(sg, scene):
"""Set all materials in scene to vertex colored."""
material_table = scene.GetMaterialTable()
for i in range(0, material_table.GetMaterialsCount()):
material = material_table.GetMaterial(i)
setup_vertex_color_material(sg, material, color_channel)
def setup_vertex_color_material(sg, material, channel):
"""Set material to use vertex color as color."""
material.AddMaterialChannel(channel)
shading_node = sg.CreateShadingVertexColorNode()
shading_node.SetVertexColorIndex(vertex_color_index)
material.SetShadingNetwork(channel, shading_node)
def process_selection(sg):
"""Process selected mesh in Blender"""
# Export scene from Blender and import it
file_path = temp_path + file
scene = export_selection(sg, file_path)
# Setup vertex color shader
setup_vertex_color_materials(sg, scene)
# Process scene
pipeline = create_pipline(sg)
pipeline.RunScene(scene, Simplygon.EPipelineRunMode_RunInThisProcess)
# Import result into Blender
import_results(sg, scene, file_path)
def main():
sg = simplygon_loader.init_simplygon()
process_selection(sg)
sg = None
gc.collect()
if __name__== "__main__":
main()
Aggregation
# Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.
# Licensed under the MIT license.
import os
import bpy
import gc
from simplygon10 import simplygon_loader
from simplygon10 import Simplygon
file = "scene.glb"
temp_path = "c:/tmp/"
# Change parameters for quality
texture_size = 4096
# Blender specific settings
color_channel = "Basecolor"
vertex_color_index = 0
def export_selection(sg, file_path):
"""Export the current selected objects into Simplygon."""
bpy.ops.export_scene.gltf(filepath = file_path, use_selection=True)
sceneImporter = sg.CreateSceneImporter()
sceneImporter.SetImportFilePath(file_path)
sceneImporter.Run()
scene = sceneImporter.GetScene()
return scene
def import_results(sg, scene, file_path):
"""Import the Simplygon scene into Blender."""
scene_exporter = sg.CreateSceneExporter()
scene_exporter.SetExportFilePath(file_path)
scene_exporter.SetScene(scene)
scene_exporter.Run()
bpy.ops.import_scene.gltf(filepath=file_path)
def create_aggregaton_pipline(sg):
"""Create aggregation pipeline with color material caster"""
aggregation_pipeline = sg.CreateAggregationPipeline()
aggregator_settings = aggregation_pipeline.GetAggregationSettings()
mapping_image_settings = aggregation_pipeline.GetMappingImageSettings()
mapping_image_settings.SetGenerateMappingImage(True)
material_settings = mapping_image_settings.GetOutputMaterialSettings(0)
material_settings.SetTextureWidth(texture_size)
material_settings.SetTextureHeight(texture_size)
mapping_image_settings.SetTexCoordGeneratorType( Simplygon.ETexcoordGeneratorType_Parameterizer )
caster = sg.CreateColorCaster()
caster_settings = caster.GetColorCasterSettings()
caster_settings.SetMaterialChannel( color_channel )
aggregation_pipeline.AddMaterialCaster( caster, 0 )
return aggregation_pipeline
def setup_vertex_color_materials(sg, scene):
"""Set all materials in scene to vertex colored."""
material_table = scene.GetMaterialTable()
for i in range(0, material_table.GetMaterialsCount()):
material = material_table.GetMaterial(i)
setup_vertex_color_material(sg, material, color_channel)
def setup_vertex_color_material(sg, material, channel):
"""Set material to use vertex color as color."""
material.AddMaterialChannel(channel)
shading_node = sg.CreateShadingVertexColorNode()
shading_node.SetVertexColorIndex(vertex_color_index)
material.SetShadingNetwork(channel, shading_node)
def remove_vertex_weights(sg, scene, vertex_color_index):
"""Remove all vertex colors of index from scene."""
scene_meshes_selection_set_id = scene.SelectNodes("SceneMesh")
scene_meshes_selection_set = scene.GetSelectionSetTable().GetSelectionSet(scene_meshes_selection_set_id)
# Loop through all meshes in the scene
for node_id in range(scene_meshes_selection_set.GetItemCount()):
scene_mesh = Simplygon.spSceneMesh.SafeCast(scene.GetNodeByGUID( scene_meshes_selection_set.GetItem(node_id)))
# Get geometry for mesh
geometry = scene_mesh.GetGeometry()
if not geometry:
continue
geometry.RemoveColors(vertex_color_index)
def process_selection(sg):
"""Remove and bake decals on selected meshes."""
# Export scene from Blender and import it
file_path = temp_path + file
scene = export_selection(sg, file_path)
# Setup vertex color shader
setup_vertex_color_materials(sg, scene)
# Aggregate optimized scene
pipeline = create_aggregaton_pipline(sg)
pipeline.RunScene(scene, Simplygon.EPipelineRunMode_RunInThisProcess)
# Clean up vertex colors
remove_vertex_weights(sg, scene, vertex_color_index)
# Import result into Blender
import_results(sg, scene, file_path)
def main():
sg = simplygon_loader.init_simplygon()
process_selection(sg)
sg = None
gc.collect()
if __name__== "__main__":
main()
